Facial fracture
1. nasalorbitalethmoid fracture(NOE fracture)
Blunt force directly over the nasal pyramid.
Commonly bilateral, but 1/3 unilateral.
The nasoorbitoethmoid (NOE) complex is the confluence of the frontal sinus, ethmoid sinuses, anterior cranial fossa, orbits, frontal bone, and nasal bones.
Long-term sequelae of NOE fractures include blindness, telecanthus, enophthalmos, midface retrusion, cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) fistula, anosmia, epiphora, sinusitis, and nasal deformity.
medial canthal tendon: 分為anterior, posterior,以及superior三個部份,包住lacrimal sac

Orbicularis oculi:分為pretarsal, preseptal,以及orbital portion三個部份
都是源自於medial canthal tendon,中止於lateral canthal tendon(除了orbital portion)

Classification
Type 1: single segment central fracture with medial canthal tendon attached.
Type 2: comminuted fracture with medial canthal tendon attached.
Type 3: comminuted fracture with avulsed medial canthal tendon

PE:
-Loss of dorsal-nasal prominence
-Glabellar, periorbital, nasal ecchymosis
-Telecanthus>35mm(眼距過寬,normal 30~32mm)
-Bowstring test: lateral traction of lower eyelid will result in telecanthus if ligament is disrupted.
-Rhinorrhea: avoid CSF leakage
-Olfactory disturbance
2. maxillary fracture(LeFort Fracture)
Le Fort I Fracture = Horizontal Fracture
Clinical:
Facial edema
Malocclusion of the teeth
Motion of the maxilla while the nasal bridge remains stable
Le Fort II Fracture = Pyramidal Fracture
Clinical:
Marked facial edema
Nasal flattening
Traumatic telecanthus
Epistaxis or CSF rhinorrhea
Movement of the upper jaw and the nose.
Le Fort III Fractures = Craniofacial Separation
Clinical:
Dish faced deformity
Epistaxis and CSF rhinorrhea
Motion of the maxilla, nasal bones and zygoma
Severe airway obstruction


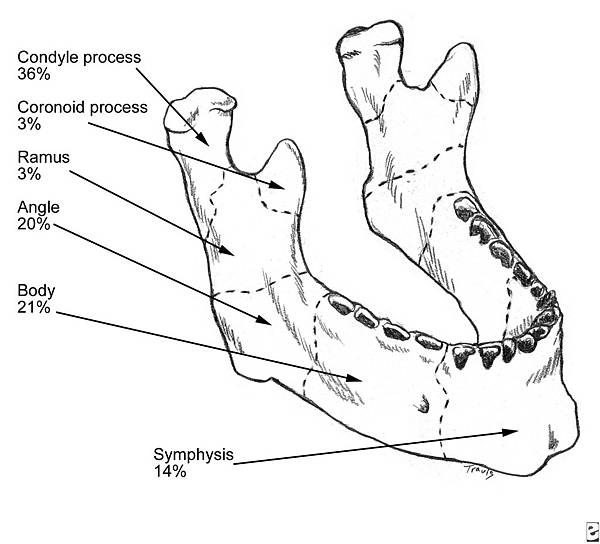
3. mandibular fracture

4. Orbital Fractures
(1). Composed of 7 bones:
Zygoma, sphenoid, ethmoid, frontal, palatine, maxilla, lacrimal
(2). Weakest structure: medial wall
(3). Superior orbital fissure: CN3, 4, 5-1, 6
(4). Inferior orbital fissure: CN5-2, sphenopalatine ganglion, inferior ophthalmic vein
Superior orbital fissure(SOF) syndrome: fractures of the SOF result in
-fixed dilated pupil (CN 3)
-upper lid ptosis (CN 3)
-loss of corneal reflex (CN 5-1)
-ophthalmoplegia (CN 4,5-1)
Orbital apex syndrome: SOF syndrome+ impairment of optic nerve
Type of orbital fractures
1. orbital floor (blow out): fractures most commonly occur at medial wall and floor of the orbit along the infraorbital groove. A fracture defect may entrap periorbital fat and possibly the inferior rectus muscle. 症狀: 1.眼週邊瘀血、腫 2.enophthalmos (若眼球仍oedema反而是proptosis) 3. infraorbital nerve anaesthesia (下眼瞼、臉頰、鼻側、上唇、上牙齦) 4.複視: 多為 vertical diplopia 5.orbital emphysema (嚴重時由sinus來)
2. orbital roof (blow in): rare, due to protection by the supraorbital rimand frontal bone. If injury to the supraorbital artery can result in a retrobulbar hematoma.
Surgical indications
-early enophthalmos>2mm
-symptomatic diplopia>2 weeks
-displaced fracture with floor defect>1 cm2
-hypoglobus: low vertical lying globe
-positive forced duction test
-oculocardiac response: nausea, vomiting, bradycardia, and syncope


 留言列表
留言列表


